Creating a Kubernetes cluster
By employing OpenStack Magnum you can create Kubernetes clusters via OpenStack, using the Breqwatr Cloud Management Panel or the OpenStack CLI.
Prerequisites
First and foremost, you need an account in
Breqwatr Cloud. Should you choose to
work from your terminal, you will also need to enable the OpenStack
CLI. In that case, in
addition to the Python openstackclient module, make sure you also
install the corresponding plugin module for Magnum. Use either the
package manager of your operating system or pip:
=== "Debian/Ubuntu"
bash
apt install python3-magnumclient
=== "Mac OS X with Homebrew"
This Python module is unavailable via brew, but you can install it
via pip.
=== "Python Package"
bash
pip install python-magnumclient
Creating a Kubernetes cluster
=== "Breqwatr Cloud Management Panel" Fire up your favorite web browser, navigate to the Breqwatr Cloud Management Panel start page, and log into your Breqwatr Cloud account. On the top right-hand side of the Breqwatr Cloud Management Panel, click the Create button. A new pane titled Create slides into view.
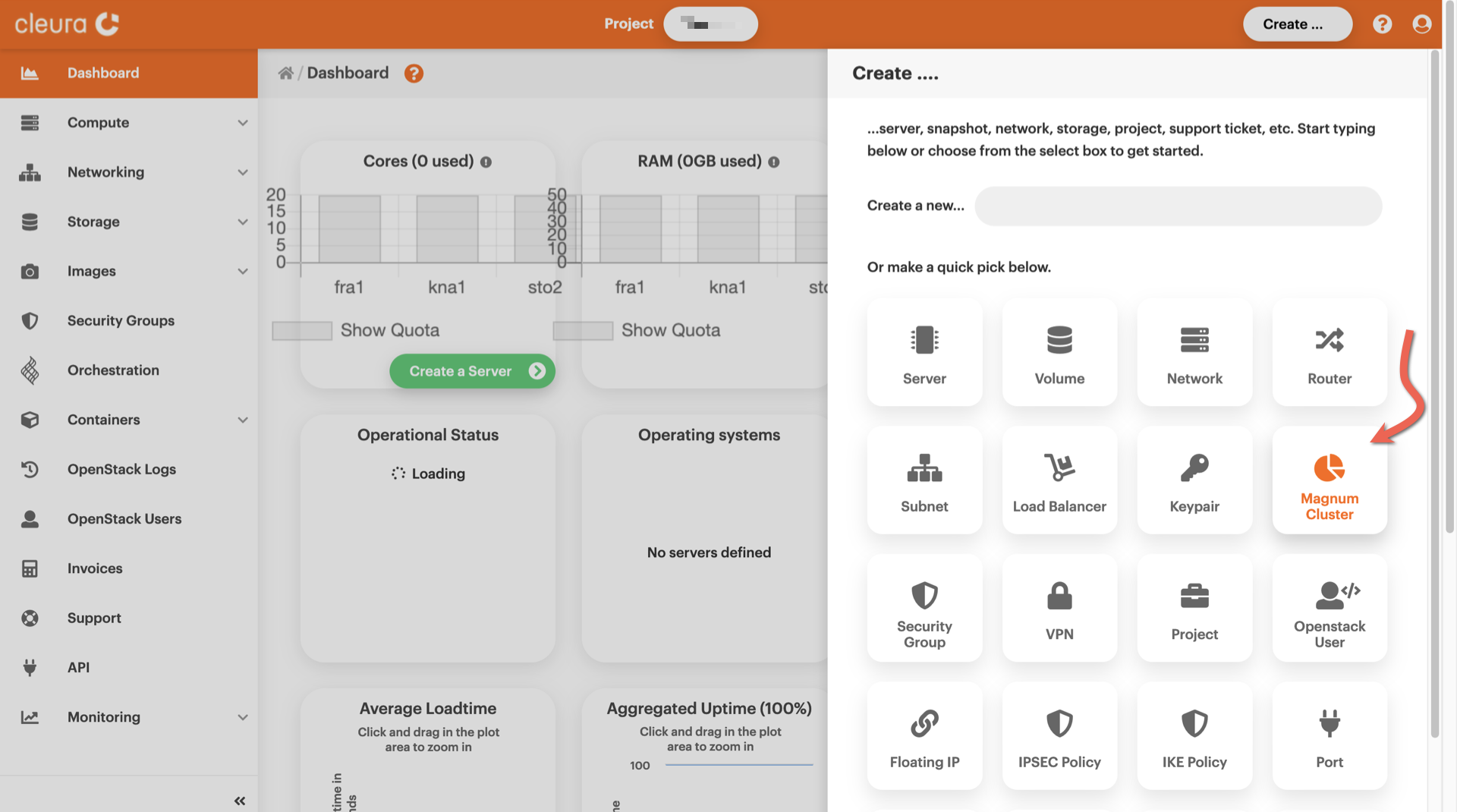
You will notice several rounded boxes on that pane, each for defining,
configuring, and instantiating a different Breqwatr Cloud object. Go ahead
and click the *Magnum Cluster* box. A new vertical pane titled *Create a
Magnum Cluster* slides over. At the top, type in a name for the new
cluster and select one of the available regions.
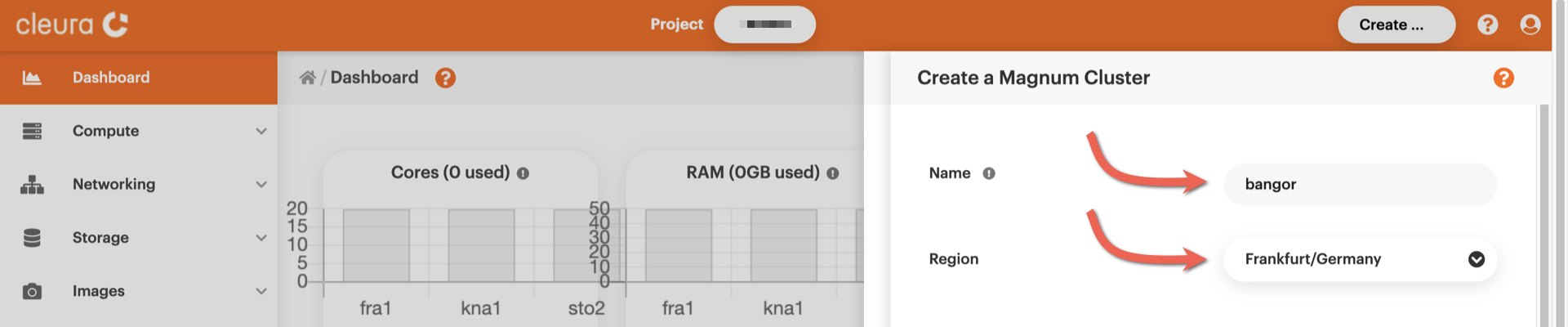
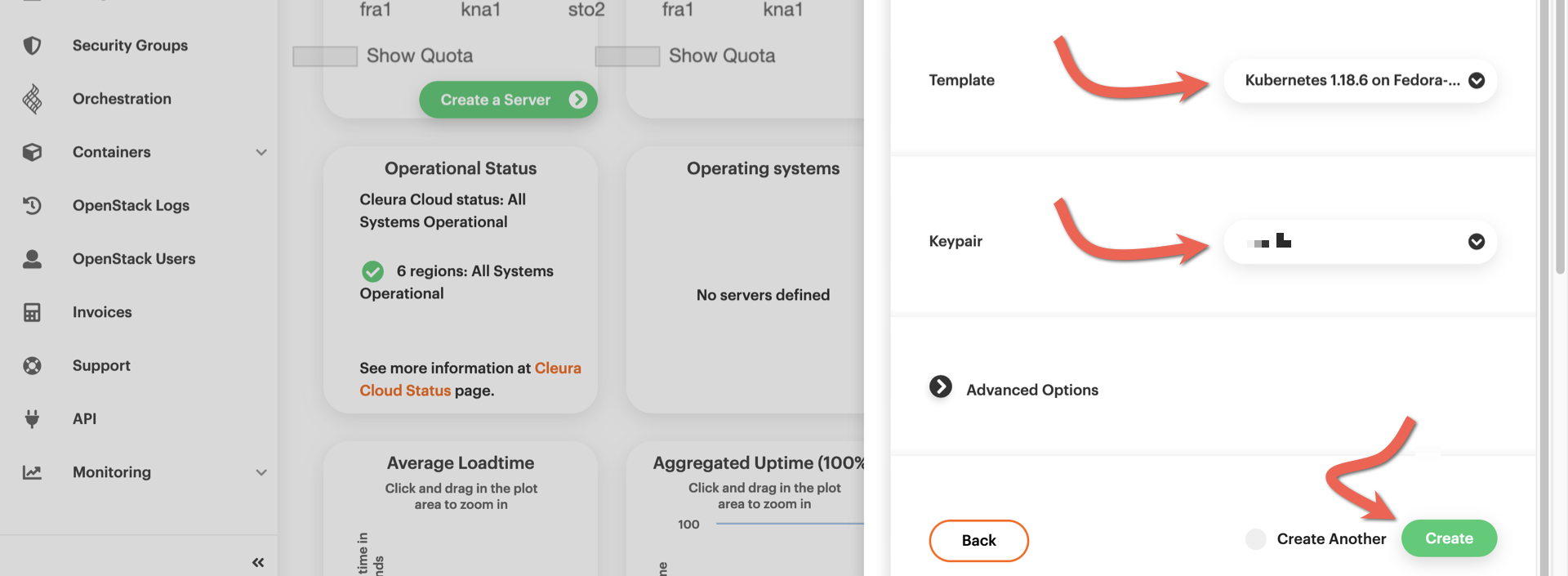
A bit further below, use the drop-down menus to select a template and a
keypair for the cluster nodes. Then, click the green *Create* button.
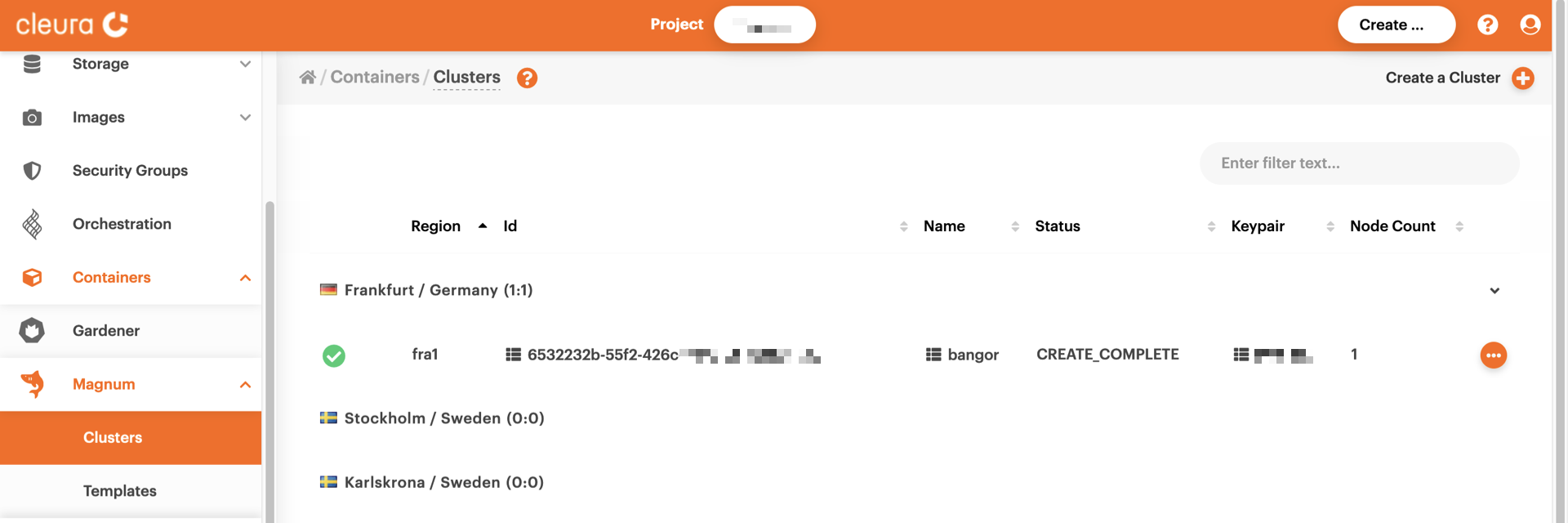
The cluster creation process begins and takes some time to complete.
While waiting, bring the vertical pane on the left-hand side of the
Breqwatr Cloud Management Panel in full view, select *Magnum* → *Clusters*, and in the main
pane, take a look at the creation progress. You can tell when the whole
process is complete by the icon at the left of the cluster row, or by
the text in the *Status* column.
=== "OpenStack CLI" A simple, general command for creating a new Kubernetes cluster with Magnum looks like this:
```bash
openstack coe cluster create \
--cluster-template $CLUSTER_TMPL \
--keypair $KEYPAIR \
$CLUSTER_NAME
```
You can now list all available templates in the region:
```bash
openstack coe cluster template list
```
```plain
+--------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------+------+
| uuid | name | tags |
+--------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------+------+
| 3f476f01-b3de-4687-a188-6829ed947db0 | Kubernetes 1.15.5 on Fedora-atomic 29 4C-8GB-20GB No Master LB | None |
| c458f02d-54b0-4ef8-abbc-e1c25b61165a | Kubernetes 1.15.5 on Fedora-atomic 29 2C-4GB-20GB No Master LB | None |
| f9e1a2ea-b1ff-43e7-8d1e-6dd5861b82cf | Kubernetes 1.18.6 on Fedora-coreos 33 2C-4GB-20GB No Master LB | None |
+--------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------+------+
```
Select the template you want by setting the corresponding `uuid`
value to the `CLUSTER_TMPL` variable:
```bash
CLUSTER_TMPL="f9e1a2ea-b1ff-43e7-8d1e-6dd5861b82cf" # just an example
```
Then, list all available keypairs...
```bash
openstack keypair list
```
```plain
+---------+-------------------------------------------------+------+
| Name | Fingerprint | Type |
+---------+-------------------------------------------------+------+
| husavik | 34:3b:58:ba:ec:95:f5:17:17:df:04:38:11:89:e6:3d | ssh |
+---------+-------------------------------------------------+------+
```
...and set the `KEYPAIR` variable to the name of the keypair you
want:
```bash
KEYPAIR="husavik" # again, this is just an example
```
Finally, decide on a name for your new Kubernetes cluster:
```bash
CLUSTER_NAME="bangor"
```
With everything in place, go ahead and create your new Kubernetes
cluster:
```bash
openstack coe cluster create \
--cluster-template $CLUSTER_TMPL \
--keypair husavik
bangor
```
If everything went well with your request for a new cluster, on your
terminal, you would see a message like the following:
```plain
Request to create cluster e0df8c62-c6f6-4c7d-b67e-33e3606e9ab6 accepted
```
The cluster creation process takes some time to complete, and while
you are waiting, you can check if everything is progressing smoothly:
```bash
openstack coe cluster list -c status
```
If everything is going well, the message you will get will be
`CREATE_IN_PROGRESS`. When Magnum has finished creating the cluster, the
message will be `CREATE_COMPLETE`.
Viewing the Kubernetes cluster
After the Kubernetes cluster is ready, you may at any time view it and get detailed information about it.
=== "Breqwatr Cloud Management Panel" Bring the vertical pane on the left-hand side of the Breqwatr Cloud Management Panel in full view, then select Magnum → Clusters. In the main pane, take a look at the row of the cluster you are interested in. In our example, there is only one cluster, hence only one row.
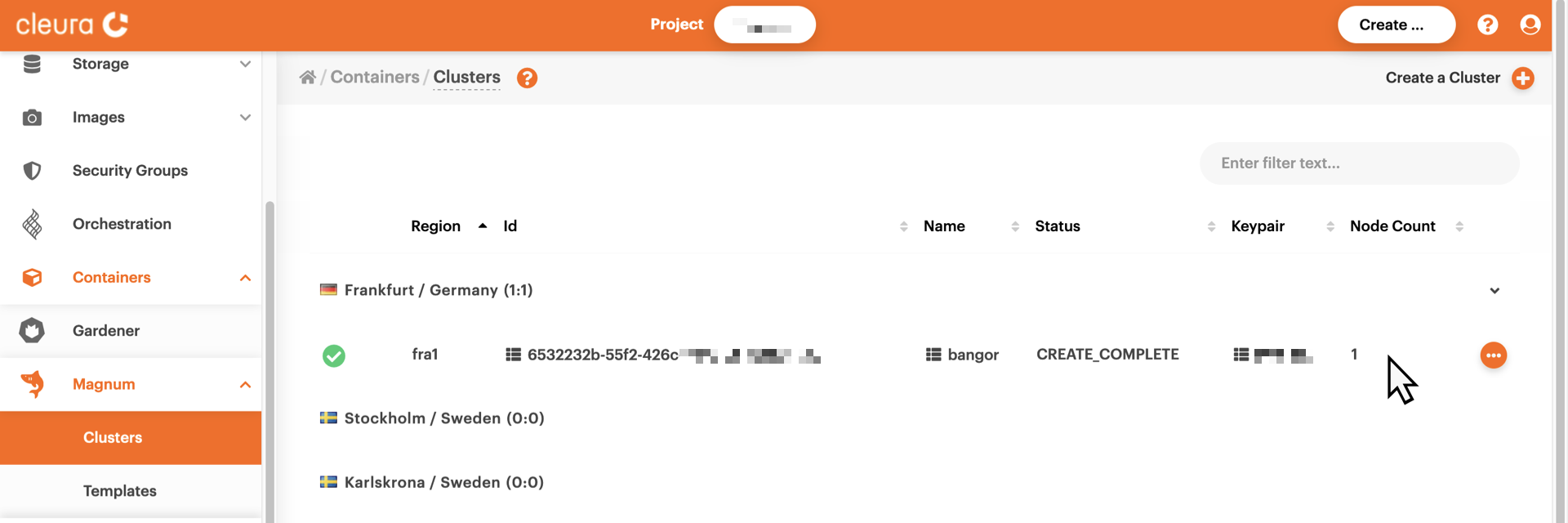
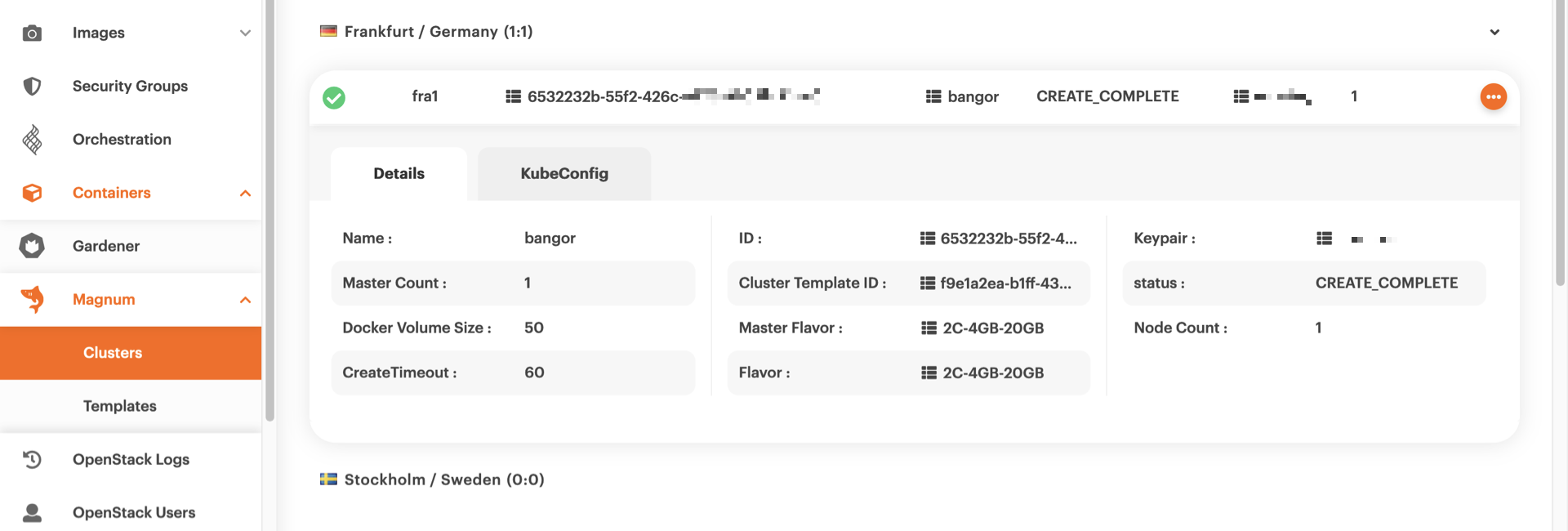
To get more information on the cluster, just click on its row.
Then, all relative information is displayed below the row.
=== "OpenStack CLI" To list all available Kubernetes clusters, type:
```bash
openstack coe cluster list
```
```plain
+---------------+--------+---------+------------+--------------+---------------+---------------+
| uuid | name | keypair | node_count | master_count | status | health_status |
+---------------+--------+---------+------------+--------------+---------------+---------------+
| e0df8c62-c6f6 | bangor | husavik | 1 | 1 | CREATE_COMPLE | HEALTHY |
| -4c7d-b67e-33 | | | | | TE | |
| e3606e9ab6 | | | | | | |
+---------------+--------+---------+------------+--------------+---------------+---------------+
```
For many more details on a specific cluster, note its name and run a
command like this:
```bash
openstack coe cluster show bangor
```
```plain
+----------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+----------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| status | CREATE_COMPLETE |
| health_status | HEALTHY |
| cluster_template_id | f9e1a2ea-b1ff-43e7-8d1e-6dd5861b82cf |
| node_addresses | ['192.0.2.105'] |
| uuid | e0df8c62-c6f6-4c7d-b67e-33e3606e9ab6 |
| stack_id | e3725aed-f665-4e8d-9409-85f5ee5e2f4a |
| status_reason | None |
| created_at | 2022-11-14T07:32:02+00:00 |
| updated_at | 2022-11-14T07:37:26+00:00 |
| coe_version | v1.18.6 |
| labels | {'kube_tag': 'v1.18.6', 'heat_container_agent_tag': 'train-stable'} |
| labels_overridden | {} |
| labels_skipped | {} |
| labels_added | {} |
| fixed_network | None |
| fixed_subnet | None |
| floating_ip_enabled | True |
| faults | |
| keypair | husavik |
| api_address | https://192.0.2.136:6443 |
| master_addresses | ['192.0.2.136'] |
| master_lb_enabled | False |
| create_timeout | 60 |
| node_count | 1 |
| discovery_url | https://discovery.etcd.io/23af721dc3ee773d2674db4881ff70cb |
| docker_volume_size | 50 |
| master_count | 1 |
| container_version | 1.12.6 |
| name | bangor |
| master_flavor_id | 2C-4GB-20GB |
| flavor_id | 2C-4GB-20GB |
| health_status_reason | {'bangor-id6nijycp2wy-master-0.Ready': 'True', 'bangor-id6nijycp2wy- |
| | node-0.Ready': 'True', 'api': 'ok'} |
| project_id | dfc700467396428bacba4376e72cc3e9 |
+----------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
```
Interacting with your cluster
Once your new Magnum-managed Kubernetes cluster is operational, you can start interacting with it.